Push to deploy a Python (Django) service via Github Actions
After using ploi to deploy a Laravel app in the past I
really enjoyed the simplicity of just using a git push to deploy my
application to staging/production. Ploi configures your Github repository to use a
webook to notify Ploi if a new commit was made. It then pulls the source and
deploys it.
While ploi does not (yet) offer to manage python/django applications, I found a few resources where this functionality is solved with Github/Gitlab actions, which I adapted to my needs.
The following steps can be used to deploy a django app via push to a
production branch.
Deployment scripts
For deployment, we make use of two scripts. One is responsible for deploying on
the server (deploy_server.sh) while the other is will push the current master
branch to production.
deploy_server.sh:
#!/bin/sh
set -e
SCRIPT=`realpath $0`
SCRIPTPATH=`dirname $SCRIPT`
PYTHON="$SCRIPTPATH/../venv/bin/python"
PIP="$SCRIPTPATH/../venv/bin/pip"
echo "Deploying application ..."
cd $(dirname $SCRIPTPATH)
# Update codebase
git fetch origin production
git reset --hard origin/production
$PIP install -r requirements.txt
# collect static stuff
$PYTHON manage.py collectstatic --noinput;
# Migrate database
$PYTHON manage.py migrate
systemctl --user restart django_deploy_test
echo "Application deployed!"
This script will
- use a virtualenv from the $PROJECT/venv folder
- fetch and reset to the
productionbranch - install all requirements
- call collectstatic and migrate
- restart the user service
Now let’s have a look at the local deploy.sh:
#!/bin/sh
set -e
(git push) || true
git checkout production
git merge master
git push origin production
git checkout master
Push workflow
To trigger the deployment via Github Actions, the following workflow can be
used, which takes preconfigured secrets, authenticates over SSH and executes
the deploy_server.sh script.
.github/workflows/main.yml
name: deploy on prod push
on:
push:
branches: [ production ]
jobs:
build:
name: Build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: executing remote ssh commands using password
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@master
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USER }}
key: ${{ secrets.PRIVATE_KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: |
/home/username/projects/django_deploy_test/deploy/deploy_server.sh
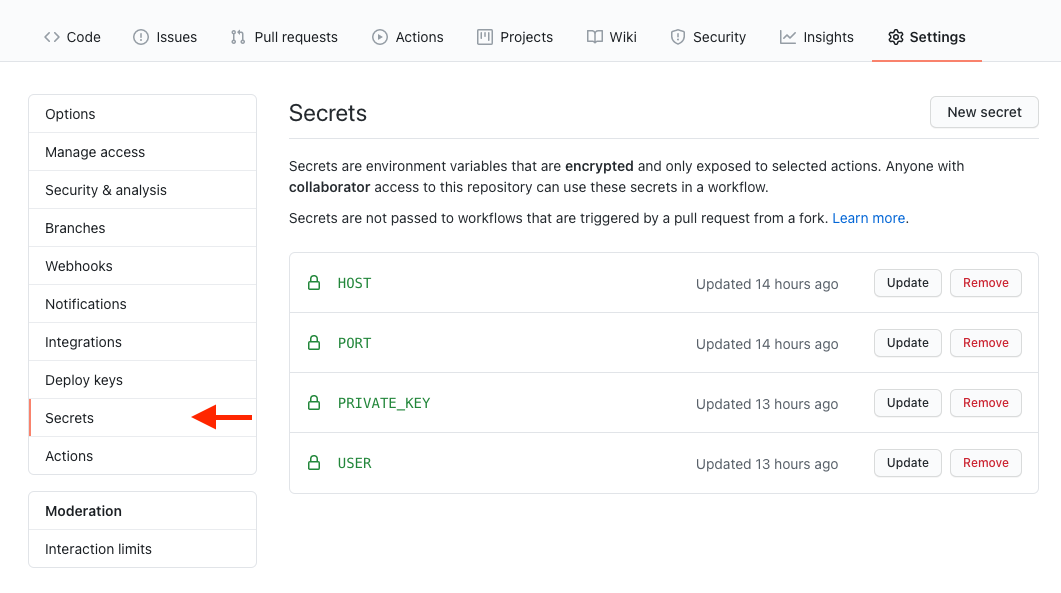
The secrets can be configured under the Settings tab in a repository:
Setting up the service
The last step is now to configure django with gunicorn as a service and enable it:
.config/systemd/user/django_deploy_test.service
[Unit]
Description=django daemon
After=network.target
[Service]
WorkingDirectory=/home/user/projects/django_deploy_test
ExecStart=/home/user/projects/django_deploy_test/venv/bin/gunicorn --access-logfile - --workers 3 --bind unix:/home/user/projects/django_deploy_test.sock django_deploy_test.wsgi:application
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Enable it via: systemctl --user enable django_deploy_test. Because this is
installed as a user service, no sudo is needed for restarting it.
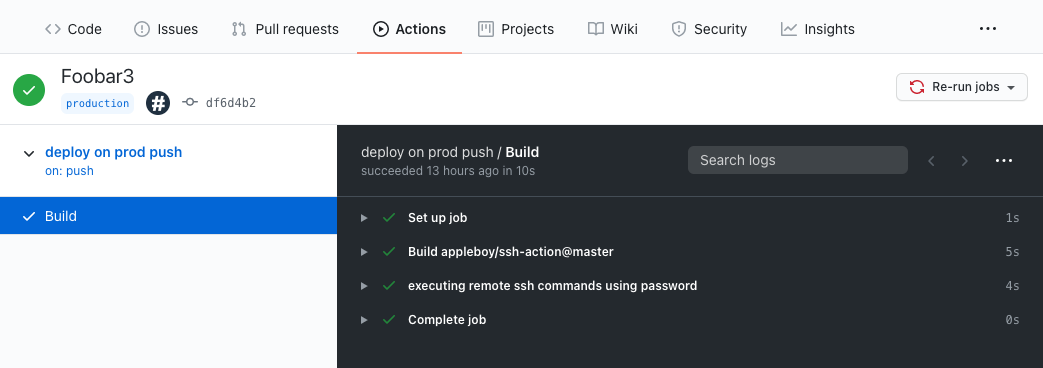
And now we are ready to go. After executing the deploy.sh script you can see
the github workflow beeing executed: